Resources
Search below for resources covering the intersection of climate engagement, social science and data analytics.
RESULTS
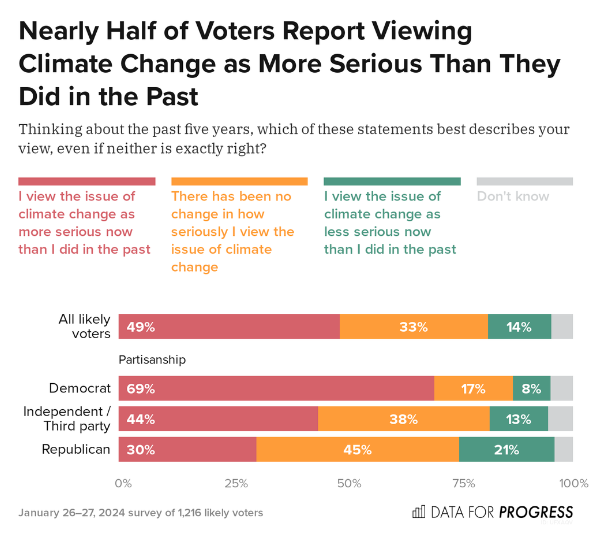
Environmental Polling Roundup - February 23rd, 2024
This post includes climate and environment headlines, data points, and key takeaways from recent public polls - including new polling on voters’ relative trust in the two parties to handle climate change and the environment, as well as new polling and consumer data about electric vehicles.
HEADLINES
Republican EV drivers outnumber Democratic EV drivers in many states, based on voter file data and vehicle records. In nine of the 31 states and DC that register voters by party, for example, more Republican voters are linked to records of electric vehicles – including insurance and repair records – than Democrats. Republicans, independents and third-party voters associated with electric vehicles also exceed Democrats in 24 of those states. There is a mix of market factors, such as consumer awareness, infrastructure, incentives and availability, that drive sales.
Environmental Polling Roundup - February 16th, 2024
This post includes climate and environment headlines, data points, and key takeaways from recent public polls - including new polls of Western voters and young conservatives.
Poll: State of The Rockies
The latest “State of the Rockies” poll finds that Western voters across party lines rate conservation issues as an important factor in their vote this year. For the first time in the poll’s history, the majority of Republicans say that conservation should be prioritized over maximizing fossil fuel production. 90% of voters in Western States support requiring oil and gas companies, rather than federal and state governments, to pay for all of the clean-up and land restoration costs after drilling is finished.
Climate conversations: how do we know if they make a difference?
Conversations about climate may be an important part of the advocacy toolkit. Larger US has recruited a cohort to be trained on these conversations. The trainees, after being trained, feel significantly better able to have climate conversations. However, evaluating the impacts of the trainees having conversations outside of the training program is difficult. The goal is to understand if the conversations affect the beliefs of people in the conversations, as well as the broader impact on society.
Environmental Polling Roundup - February 9th, 2024
This post includes climate and environment headlines, data points, and key takeaways from recent public polls - including new polling on ESG/responsible investing, offshore wind, electric vehicles, and the Green New Deal.
Poll: Here’s How To Get Republicans Behind Electric Vehicles
Cultural attitudes drive the partisan split on electric vehicles, as Democrats and Republicans disagree more about whether electric vehicles are for “people like them” than on any of the specific benefits or downsides of EVs. In this new survey of Americans with household incomes of $50,000 or more (intended to approximate the market for new cars in the U.S.), Democrats and Republicans have very similar answers when asked to name their two greatest concerns about owning an electric vehicle.
Americans in coastal counties have overwhelmingly positive attitudes about offshore wind energy and support offshore wind near where they live. Energy independence is a strong rationale for expanding offshore wind, though there are concerns about impacts on wildlife. Surveying Americans who live in coastal counties, they find that these Americans have overwhelmingly positive attitudes about offshore wind and its expansion – including in their own areas: 68% support the construction of offshore wind farms to harness wind; energy in U.S.
Poll: Five Years After Its Introduction, the Green New Deal Is Still Incredibly Popular
Voters consistently support the idea of a Green New Deal when they learn what it would contain. Nearly two-thirds of voters (65%) – including majorities of Democrats (85%) and independents (64%), as well as a plurality of Republicans (45%) – support a Green New Deal when provided with the information below. Support for the Green New Deal also stands up to scrutiny.
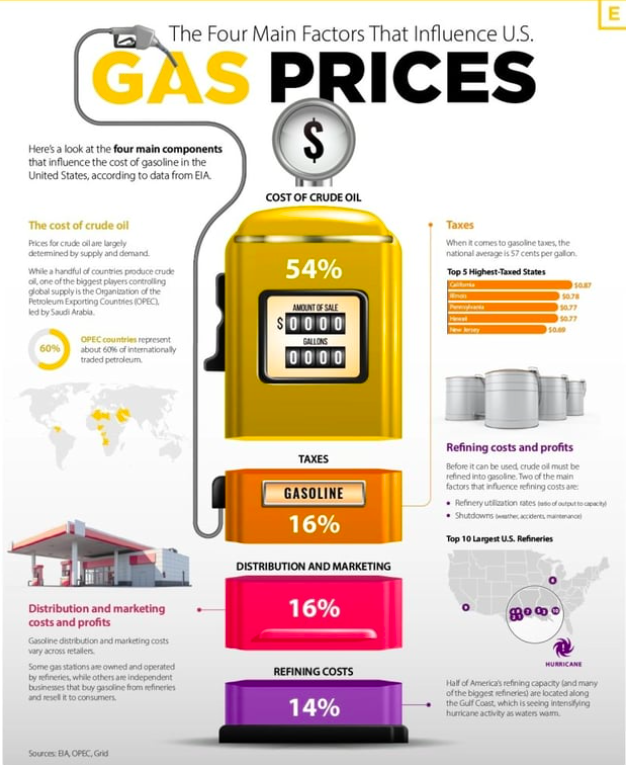
Here are the terms and narratives the fossil fuel industry is using to obstruct climate action. The fossil fuel industry haven’t really come up with new spin in about a century, just slightly updated versions of the same old stories on repeat, including: “Climate Policy Makes Gas Prices Higher,” “The LNG Boom Delivers Energy Security and Pricing Stability,” “Fossil Fuel Development Will Solve Poverty in the Global South (particularly Africa),” “Wind Turbines Kill Birds,” “Offshore Wind Kill Whales and Other Marine Species.” Misleading terms are also described.
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 3
- Next page